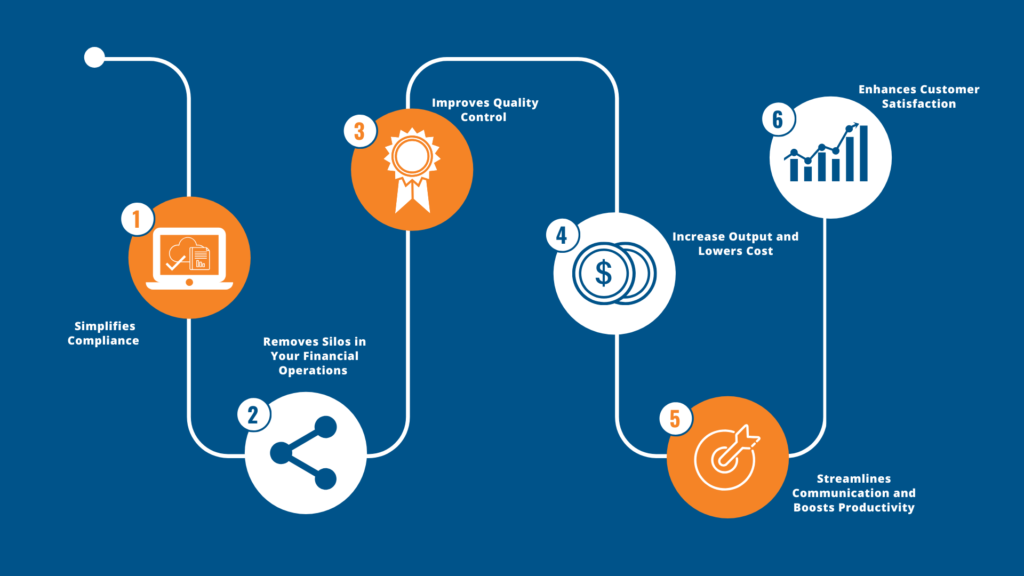
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are comprehensive software solutions that integrate various business processes, including finance, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management. Traditionally, ERP systems have been deployed on-premises, requiring substantial hardware investments, ongoing maintenance, and dedicated IT staff. However, the advent of cloud-based ERP systems has revolutionized the way businesses manage their operations.
Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on remote servers and delivered over the internet, eliminating the need for significant on-site infrastructure. This architectural shift brings several advantages over traditional on-premises ERP systems. One of the primary benefits is accessibility; cloud-based ERP solutions can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating real-time data sharing and collaboration across global teams. This is particularly advantageous for manufacturers, who often operate multiple facilities in different locations.
Scalability is another critical advantage. Cloud-based ERP systems can easily scale up or down to meet the changing needs of a business. As manufacturers grow, they can add new users, features, or modules without the need for significant hardware upgrades or complex installations. This flexibility allows manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands and operational changes.
Cost-effectiveness is a significant consideration for any business, and cloud-based ERP systems offer a more economical solution compared to traditional on-premises systems. They typically operate on a subscription-based model, reducing the need for large upfront capital expenditures. Additionally, the cloud provider handles system maintenance, updates, and security, further lowering the total cost of ownership.
The integration capabilities of cloud-based ERP systems are particularly beneficial for manufacturers. These systems can connect with other cloud-based applications, such as supply chain management tools and customer relationship management software, creating a unified platform that enhances operational efficiency. By leveraging the power of cloud-based ERP systems, manufacturers can streamline their processes, improve productivity, and gain a competitive edge in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Key Features of Cloud-Based ERP Systems for Manufacturers
Cloud-based ERP systems offer a multitude of features tailored to meet the unique needs of manufacturers. One of the most critical modules is inventory management, which provides real-time tracking of raw materials and finished goods. This feature ensures optimal stock levels, reduces the risk of overstocking or stockouts, and improves overall inventory accuracy. By leveraging advanced analytics, manufacturers can predict demand more accurately and align their inventory strategies accordingly.
Another essential feature is production planning. Cloud-based ERP systems enable manufacturers to schedule production runs efficiently, manage work orders, and monitor progress in real-time. This level of oversight helps in minimizing downtime, optimizing resource utilization, and ensuring timely delivery of products. Additionally, these systems can integrate with various manufacturing execution systems (MES) to further streamline operations.
Quality control is another crucial module offered by cloud-based ERP systems. Manufacturers can set quality standards, conduct inspections, and track non-conformances seamlessly. This ensures that products meet stringent quality requirements, reducing the likelihood of defects and recalls. Automated reporting and compliance tracking also help in adhering to industry regulations and standards.
Supply chain management is vital for manufacturers, and cloud-based ERP systems excel in this area by offering end-to-end visibility across the supply chain. From procurement to delivery, these systems facilitate efficient coordination with suppliers, optimize logistics, and enhance demand forecasting. Improved supply chain transparency leads to better decision-making and reduced operational risks.
Financial management is a cornerstone of any ERP system, and cloud-based solutions are no exception. These systems offer comprehensive financial modules that include accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting. Real-time financial data helps manufacturers make informed decisions, manage costs, and improve profitability. Integration with other modules ensures that financial data is always up-to-date and accurate.
Real-world examples illustrate the transformative impact of these features. For instance, a mid-sized automotive parts manufacturer implemented a cloud-based ERP system and reported a 20% reduction in production costs within the first year. The system’s real-time analytics enabled the company to identify inefficiencies and optimize their production processes.
Challenges in Implementing Cloud-Based ERP Systems
While the adoption of cloud-based ERP systems offers numerous benefits to manufacturers, the implementation process is not devoid of challenges. A primary concern for many manufacturers is data security. Transitioning sensitive business data to the cloud can raise fears about data breaches and unauthorized access. To mitigate these concerns, it is crucial to choose a vendor that prioritizes robust cybersecurity measures, including data encryption, regular security audits, and compliance with industry standards.
Integration with existing systems is another significant challenge. Many manufacturers operate with legacy systems that may not be readily compatible with new cloud-based ERP solutions. This incompatibility can lead to data silos and operational inefficiencies. A phased implementation approach can help address these issues. By gradually migrating functions to the cloud and ensuring thorough testing at each stage, manufacturers can minimize disruptions and ensure a smoother transition.
User training also presents a critical challenge. Employees accustomed to legacy systems may find it difficult to adapt to the new cloud-based ERP environment. Comprehensive training programs are essential to ensure that users are comfortable and proficient with the new system. These programs should be tailored to different user roles and should include hands-on training sessions, user manuals, and ongoing support to address any issues that arise post-implementation.
Change management is another hurdle that manufacturers must overcome. Implementing a cloud-based ERP system often requires significant changes to business processes and workflows. Resistance to change can impede the successful adoption of the new system. To counteract this, it is important to involve key stakeholders early in the decision-making process and to maintain open lines of communication throughout the implementation. By fostering a culture of collaboration and transparency, manufacturers can encourage buy-in and reduce resistance.
In conclusion, while implementing cloud-based ERP systems can be challenging, these obstacles are not insurmountable. By selecting the right vendor, adopting a phased implementation strategy, investing in user training, and prioritizing change management, manufacturers can effectively navigate these challenges and fully leverage the benefits of cloud-based ERP systems.
Future Trends in Cloud-Based ERP for Manufacturing
The manufacturing sector is continually evolving, and the integration of advanced technologies with cloud-based ERP systems is at the forefront of this transformation. Emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and Machine Learning (ML) are set to revolutionize how manufacturers operate and manage their processes.
AI is becoming a critical component in modernizing cloud-based ERP systems. With its ability to analyze vast amounts of data, AI can provide valuable insights that aid in decision-making, optimize production schedules, and enhance supply chain management. Predictive analytics, powered by AI, allow manufacturers to foresee potential issues and address them proactively, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
IoT, another transformative technology, plays a crucial role in connecting various devices and machinery within a manufacturing ecosystem. IoT-enabled ERP systems facilitate real-time monitoring and control of production lines, leading to improved operational visibility and efficiency. Data collected from IoT sensors can be integrated into ERP systems to enhance inventory management, track asset performance, and ensure product quality.
Machine Learning, a subset of AI, further augments cloud-based ERP systems by enabling them to learn from data patterns and improve over time. ML algorithms can enhance demand forecasting, optimize resource allocation, and streamline maintenance schedules. By leveraging ML, manufacturers can achieve a higher degree of automation and precision in their operations.
Real-time analytics, driven by the integration of AI, IoT, and ML, empower manufacturers with actionable insights into their processes. This holistic approach enables better decision-making, improved customer satisfaction, and greater agility in responding to market changes. The ability to access real-time data from anywhere via cloud-based ERP systems ensures that manufacturers can stay competitive in an increasingly dynamic environment.
To stay ahead, manufacturers must adopt these future trends and continuously innovate. By embracing AI, IoT, and ML, they can enhance their cloud-based ERP systems, achieve greater operational efficiency, and maintain a competitive edge in the market. The future of manufacturing lies in the seamless integration of these advanced technologies, leading to smarter, more efficient, and resilient manufacturing processes.