Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing represents a paradigm shift in the way digital resources are utilized and managed. At its core, cloud computing refers to the on-demand availability of computing resources, such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and more, over the internet. This eliminates the need for organizations to invest heavily in physical infrastructure and allows them to scale resources up or down based on their needs.
Characterized by its scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, cloud computing has become essential in various sectors. The three primary types of cloud services are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, PaaS offers hardware and software tools over the internet, and SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis.
The evolution of cloud computing can be traced back to the 1960s, with the development of time-sharing and virtualization technologies. However, it wasn’t until the late 1990s and early 2000s that modern cloud computing began to take shape, significantly transforming the technology landscape. Companies like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft have played pivotal roles in this transformation, making cloud services widely accessible and affordable.
Cloud infrastructure relies heavily on virtualization, which allows multiple virtual machines to run on a single physical machine. This maximizes resource utilization and provides a level of abstraction between the hardware and the user. Data centers, housing these physical machines, serve as the backbone of cloud computing, ensuring data availability, redundancy, and security. Cloud storage, a fundamental component, enables users to store and retrieve large volumes of data seamlessly over the internet.
Understanding these basic concepts of cloud computing is crucial as we explore its specific applications in online education. The ability to provide scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions has revolutionized how educational content is delivered and consumed, paving the way for a new era of learning.
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Online Education
Cloud computing has revolutionized online education by providing numerous advantages that enhance both the teaching and learning experience. One of the most significant benefits is scalability and flexibility. Educational institutions can easily scale their offerings to accommodate a growing number of students without the need for investing in additional physical infrastructure. This flexibility allows schools and universities to adapt swiftly to changing demands, such as surges in enrollment or the need for new courses, ensuring that educational services remain uninterrupted.
Cost-effectiveness is another critical advantage of cloud computing in the education sector. By leveraging cloud-based solutions, institutions can significantly reduce the costs associated with maintaining and upgrading physical IT infrastructure. Instead of investing in expensive hardware and software, schools can opt for subscription-based models that provide access to the latest technologies and tools. This approach not only lowers operational costs but also allows educational institutions to allocate resources more efficiently toward enhancing the quality of education.
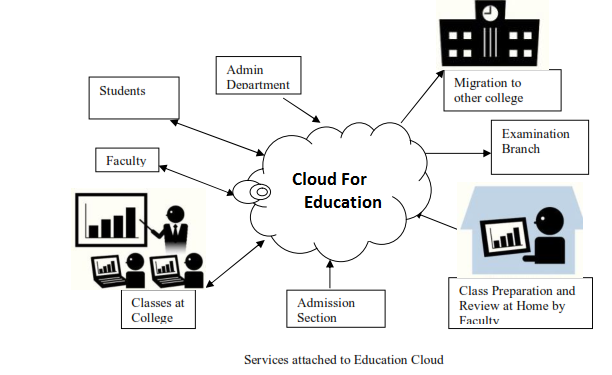
Cloud computing also enhances accessibility to educational resources. Students and teachers can access course materials, assignments, and other resources from any device with an internet connection, anytime and anywhere. This level of accessibility breaks down geographical barriers, enabling a global audience to participate in online education. It ensures that learning is not confined to the classroom and can continue seamlessly, irrespective of location.
Moreover, cloud computing facilitates real-time collaboration between students and teachers. Through cloud-based platforms, learners can engage in interactive sessions, share documents, and collaborate on projects with ease. These tools support a collaborative learning environment, promoting active participation and engagement. Features such as instant messaging, video conferencing, and shared workspaces help create a more dynamic and interactive educational experience.
In summary, the integration of cloud computing in online education offers significant benefits, including scalability, cost-effectiveness, improved accessibility, and enhanced collaboration. By leveraging these advantages, educational institutions can provide a more flexible, efficient, and inclusive learning environment for students worldwide.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous advantages that cloud computing brings to online education, its adoption is not without challenges. One of the most pressing issues is data privacy and security. Educational institutions must ensure that students’ personal information and academic records are protected from unauthorized access and cyber threats. The rise in cyberattacks on educational platforms has made robust cybersecurity measures imperative. Institutions need to invest in advanced encryption technologies and continuous monitoring systems to safeguard sensitive data.
Another significant challenge is the digital divide. While cloud computing offers scalable and flexible solutions, not all students have equal access to high-speed internet or the necessary devices. This disparity can exacerbate educational inequalities, leaving some students at a disadvantage. Efforts to bridge this gap are crucial, including governmental and institutional initiatives to provide broader access to technological resources.
Dependency on internet connectivity is another consideration. Reliable and consistent internet access is a prerequisite for effective cloud-based education. In regions where connectivity is unstable or limited, students and educators may face interruptions, affecting the learning experience. Developing offline capabilities and ensuring alternative access methods can help mitigate this issue.
Concerns about the reliability and uptime of cloud services also merit attention. Although cloud providers aim for high availability, service outages can occur, disrupting the educational process. Institutions should evaluate the reliability of their chosen cloud services and have contingency plans in place for potential downtimes.
Regulatory compliance is another critical factor. Educational institutions must adhere to data protection regulations such as GDPR, FERPA, and others relevant to their region. Ensuring compliance with these regulations requires a thorough understanding of legal requirements and the implementation of appropriate data management practices.
Finally, governmental policies play a pivotal role in shaping the use of cloud technology in education. Supportive policies can foster innovation and adoption, while restrictive regulations may hinder progress. Collaboration between educational institutions, cloud providers, and policymakers is essential to create a conducive environment for the effective use of cloud computing in education.
Future Trends and Innovations
The landscape of online education is continually evolving, driven by advancements in cloud computing. One of the most promising trends is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to create personalized learning experiences. These technologies can analyze student data to tailor educational content, providing customized learning paths that cater to individual strengths and weaknesses. This not only enhances engagement but also significantly improves learning outcomes.
Big data analytics is another transformative force in online education. By leveraging vast amounts of data generated by students, educators can gain deep insights into learning behaviors and performance metrics. This data-driven approach enables the identification of trends and patterns that can inform curriculum design and instructional strategies, ultimately leading to more effective teaching methods and improved student success rates.
Virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) are poised to offer immersive learning environments that can revolutionize the way students interact with educational content. These technologies can simulate real-world scenarios, providing experiential learning opportunities that are both engaging and informative. For instance, medical students can practice surgical procedures in a virtual environment, while history students can explore ancient civilizations through augmented reality experiences.
Blockchain technology is also gaining traction in the realm of online education. Its potential to securely verify academic credentials can address issues of fraud and misrepresentation. By providing a decentralized and tamper-proof system for recording educational achievements, blockchain can enhance the trust and credibility of online degrees and certifications.
The evolution of hybrid learning models, which combine online and in-person education, is another significant trend. These models offer the flexibility of online learning while retaining the benefits of face-to-face interaction. Cloud computing facilitates the seamless integration of these hybrid approaches, enabling institutions to offer a more versatile and inclusive educational experience.